A 23 yr old male patient with paraparesis
You can find the entire real patient clinical problem in this link here:https://vaish7.blogspot.com/2020/05/medicine.html?m=1
The following are my views regarding this case:-
The problems that I found are:
Current issues:1.Weakness of bilateral lower limbs since 5 days.
2.Tingling and numbness of lower limbs since 5 days.
3.Vomitings 5 days back with 3-4 episodes,non-projectile,non bilious,food particles is the content.
4.Sudden fall when he got up.
Previous issues:
1.Gluteal abscess(operated 5 months back)
2.Scrotal abscess since ( incision and drainage 10 days)
PAST HISTORY:
-No similar complaints in the past
-H/O multiple sexual partners
-Auto driver ( high risk behaviour)
-No history of asthma,CAD,HTN,DM.
REASONS FOR THE COMPLAINTS:
Reason for weakness,tingling & numbness might involve pathology related to nerves,muscles or neuro muscular junctions
EXAMINATION:
General examination:
No pallor,no icterus,no cynaosis,clubbing,lymphadenopathy.edema.
Temperature-afebrile
BP-120/80 mm Hg
PR-80 bpm
Systemic examination:
Rs bae +nvbs hears
P/a soft,non tender
CNS- conscious
Speech-normal
cranial nerves intact
MOTOR SYSTEM:
Right Left
Bulk : Normal Normal
Tone: ul. normal. Normal
LL. hypotonia hypotonia
Power rt. lt
ul. 5/5. 5/5
LL. 2/5. 0/5
Reflexes.
Superficial reflexes
Right. Left
Corneal. P P
Conjunctival P P
Abdominal. P P
Plantar Extensor Extensor
Extensor plantar reflex:Which indicates positive babinski sign in which the underlined nervous system and brain condition causes the reflexes to react abnormally.
Deep tendon reflexes:
Right. Left
Biceps. 2+ 1+
Triceps. 2+ 1+
Supinator. 3+ 2+
Knee 3+ 2+
Ankle. 3+ 2+
jaw jerk. 1+. 1+
-decreased deep tendon reflexes.
ankle clonus present. absent
Causes of clonus: might be due to interferences in upper motur neurons like stroke,multiple sclerosis (or) Metabolic alterations which results in hepatic failure or serotonin syndrome.
Primitive reflex -absent
Involuntary movements - absent
As there are no involuntary movements it indicates that there is no underlined pathology in the brain stem;which means brainstem is intact.
SENSORY SYSTEM - normal
CEREBELLUM
titubation - absent
Nystagmus- absent
Intensional tremors - absent
Pendular knee jerk - absent
Coordination test -normal
MENINGIAL SIGNS
Neck stiffness - negative
Kernigns sign - negative
Brudzinkis sign - negative
INVESTIGATIONS
HBS AG: negative
ANTIHCV ANTIBODIES: nonreactive
HIV : non reactive
HEMOGRAM :
HB -15.5gm/dl
Platelets- 2.23 lakhs/cumm
TLC- 9600cells/cumm
Lymphocytes 15%
LFT
TO.BIL.- 0.82mg/dl
DI.BIL.- 0.21gm/dl
SGOT.- 80IU/LIT
SGPT.- 10IU/LIT
ALK.PH.- 192IU/LIT
TO.PR 7.5gm/dl
A 4gm/dl
A/G RATI 1.19
RFT
UREA.- 16mg/dl
CREATININE.- 0.6mg/dl
URIC ACID- 3.7mg/dl
CALCIUM.- 9.4mg/dl
PHOS.- 4.6mg/dl
SODIUM.- 136meq/lit
Potassium- 3.9meq/lit
The above investigations reveal : Decreased creatinine
high SGOT levels
high ALP levels
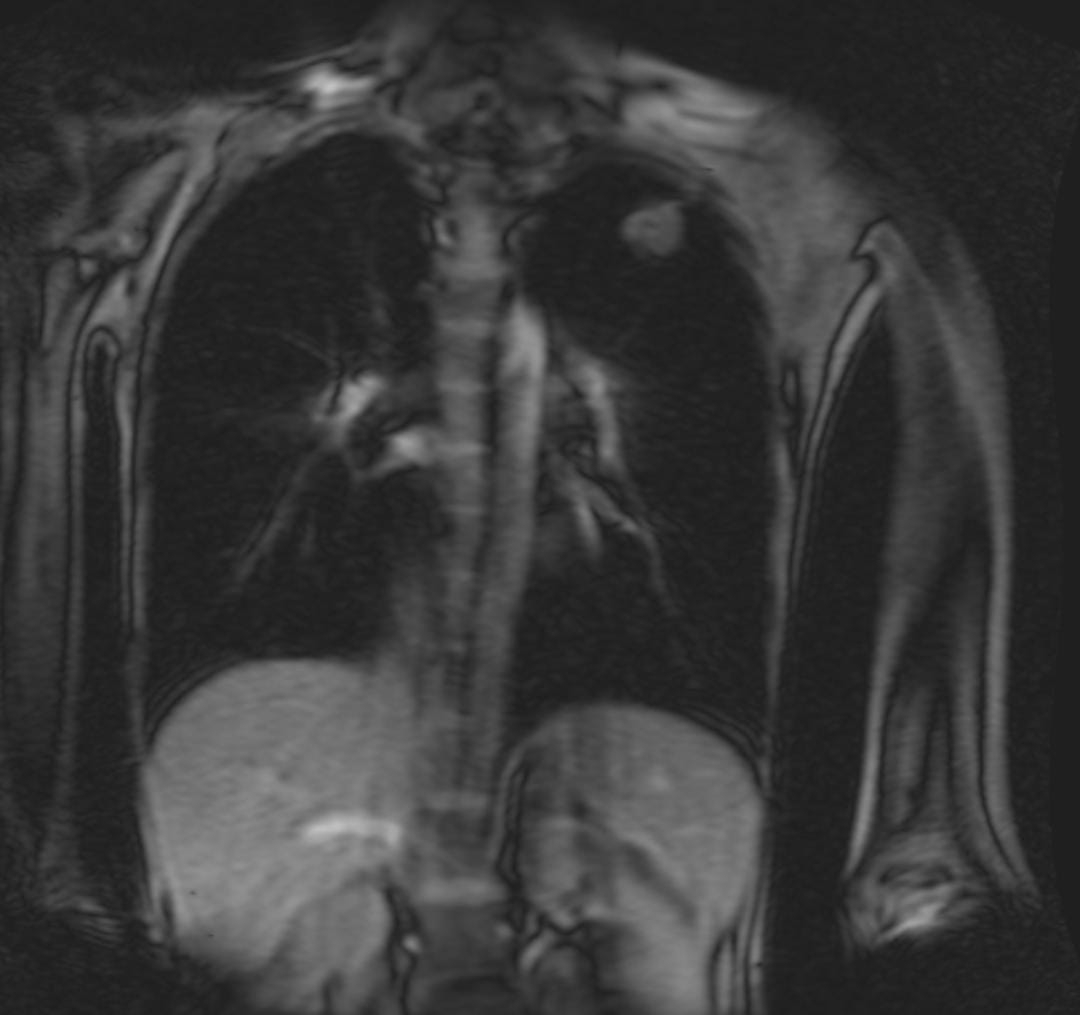
X ray images
MRI Images of the above patient are:
-The x-rays and MRI shows meningeal enhancement or exudates and lesions in MRI,multiple nodules in pulmonary apices.
-it is suggestive of pulmonary kochs and disseminated tuberculosis.
From the above findings and investigations we can conclude that:
The patient might have pulmonary tuberculosis which disseminated to the brain and the spinal cord that resulted in the present symptoms of weakness,numbness,tingling sensation of both the lower limbs,and vomitings& abscess in associated regions such as gluteal region,left psoas muscle and scrotum.
DIAGNOSIS: POTT'S DISEASE
It is also known as tuberculosis spondylitis,is a rare infectious disease of the spine which is typically caused by extra spinal infection.It is a combination of osteomyelitis and arthritis which involves multiple vertebrae.
Neurological Signs
*Neurologic abnormalities occur in 50% of cases and can include spinal cord compression with the following:
Paraplegia
Paresis
Impaired sensation
Nerve root pain
Cauda equina syndrome
Spinal Deformities
Almost all patients with Pott’s disease have some degree of spine deformity with thoracic kyphosis being the most common.
*Presentation in People Infected with HIV:
As he have a history of sex with multiple partners,HIV also plays an important role.
The clinical presentation of spinal tuberculosis in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is similar to that of patients who are HIV negative; however, spinal TB seems to be more common in persons infected with HIV.[1]
*Associated Co-morbidities:-
Immunosuppressive Disorders
HIV/AIDS
TB
Gastrectomy
Peptic Ulcer
Drug Addiction
Alcoholism
Malnourishment
Low socioeconomic status.
In this patient L4 and L5 are involved
The Pathology of the disease:
TREATMENT :
T.ATT 3 tabs/day fdc-Anti-tubercular treatment
T.Benadon 40mg/od
T.pregabalin 75mg/po/h/s-to treart nerve pain,spinal cord injury.
OINT.MEGAHEAL FOR LOCAL APPLICATION
SITZ BATH WITH BETADINE TID
FREQUENT CHANGE OF POSITION
Treatment should be continued till the patient is cured.
1) Where are the anatomical locations for the cause of the paraparesis of the patient?
-It might be upper motor or lower motor neuron lesion as he have symptoms of both.
-extensor plantar response,parasis of movement are suggestive of upper motor neuron lesion
-Hypotonia,hyporeflexes,no involuntary movements suggestive of lower motor neuron lesion.
2) What is the most likely pathology and etiology in that anatomical location?
-it might be the tubercles formed at that site due to disseminated tuberculosis.
3) What are the therapeutic options in such situations?
-ANTI-TUBERCULAR treatment is the main stay of the treatment.And drugs such as pregabalin to treat the spinal cord injury.
4) Please share questions that come to your mind upon going through each of the cases.
1.Why does patient have no prior complaints of pulmonary TB such as cough,fever.?
2.Though the MRI shows exudations in meninges,there are no meningial signs.
3.As the investigations show elevated liver enzymes,is there any hepatic failure?
4.Is it a upper motor or lower motor lesion as the symptoms of both are present?
.









Comments
Post a Comment